BRSR Assurance: Ensuring Transparency from the Lens of Business

BRSR Assurance: Ensuring Transparency from the Lens of Business
A Guide to Understanding Benefits, Types, Providers, And Success of BRSR Assurance Ensuring Increased Efficiency
- Last Updated
Sustainability consciousness has surged to the forefront of corporate agendas, prompting the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) to mandate Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Reporting in the erstwhile Business Responsibility Reporting (BRR) and now in Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR). As organizations prepare to meet these obligations, we examine the importance of accuracy and compliance in BRSR assurance from a business standpoint. To begin, let’s delve into the evolution of BRSR and BRSR Assurance Compliance. Below is the tabulation of their developmental journey.
Evolution of BRSR and BRSR Assurance Compliance
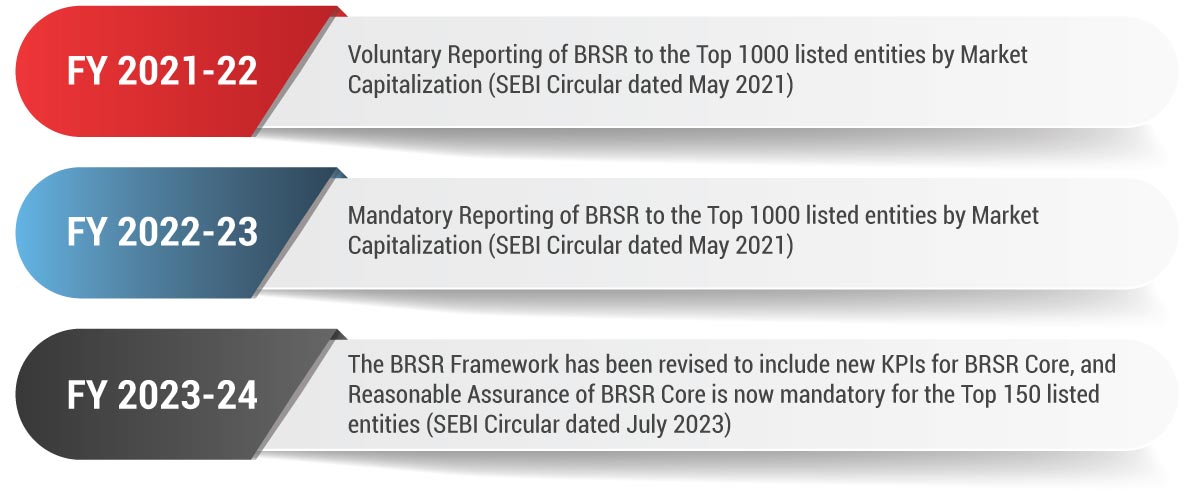
In recent years, with investors increasingly considering ESG parameters in their investment decisions, ESG investing has become quite mainstream. As stakeholders place reliance on disclosures made in BRSR, assurance becomes key for enhancing credibility and investor confidence. The aim is to mitigate greenwashing risks and facilitate easier compliance. Against this backdrop, to achieve the twin objectives of improving credibility and limiting the cost of compliance, SEBI has introduced a framework for Reasonable Assurance known as the BRSR Core.
The BRSR Core is a subset of the broader BRSR, comprising a set of key performance indicators (KPI) and metrics across nine ESG attributes. The outlined KPIs in the BRSR Core are quantifiable to the greatest extent possible, aiming to facilitate comparability of disclosures.
Nine ESG Attributes of BRSR Core

To align with SEBI’s directive and ensure credibility in sustainability reporting, listed entities are required to adhere to the prescribed glide path for Reasonable Assurance of the BRSR Core, as outlined below.
BRSR Core Reasonable Assurance Glide-Path
| Financial Year | Applicability (By Market Capitalization) |
|---|---|
| FY 2023-24 (Current Year) | Top 150 Listed entities |
| FY 2024-25 | Top 250 Listed entities |
| FY 2025-26 | Top 500 Listed entities |
| FY 2026-27 | Top 1000 Listed entities |
In this blog, we aim to simplify and explore the principles of BRSR Assurance, offering practical insights to equip your company for assurance compliance.
What is BRSR Assurance?

Related Read: The Rise of BRSR Reporting in India: Key Challenges, Implications and Strategies for Businesses
BRSR Assurance is an independent examination of information presented by the company in their BRSR report. As per Standard on Sustainability Assurance Engagement (SSAE) 3000, “Assurance Engagement is an engagement in which a practitioner aims to obtain sufficient and appropriate evidence to express a conclusion designed to enhance the degree of confidence of the intended users other than the responsible party about the subject matter information”. The intent is to express a conclusion designed to enhance the degree of confidence of the intended users and stakeholders. Broadly speaking, BRSR Assurance for a BRSR Report is akin to Limited Review or Statutory Audit for Financial Statements.
Why is BRSR Assurance Relevant?
Engaging in BRSR Assurance ensures compliance, builds reputation and creates value for stakeholders. Listed below are the direct and indirect benefits of BRSR Assurance:
Advantages of BRSR Assurance
1. Compliance with SEBI LODR Regulations
Listed entities, as per the glide path specified above are mandated to undertake reasonable assurance of the BRSR Core. Non-compliance with SEBI LODR Regulations can result in penalties and serious consequences.
2. Builds Trust and Confidence in Stakeholders
Obtaining assurance enhances stakeholders’ confidence in the data reported by the company. Taking the route of assurance will level up your ESG commitment and demonstrate transparency and credibility.
3. Optimize ESG Ratings
BRSR Assurance enhances the credibility of a company’s ESG practices, positively influencing ESG ratings by providing external validation. The accuracy and reliability of reported data are ensured through the assurance process, contributing to improved data quality and informed ESG Ratings. ESG rating providers also offer Core ESG Ratings, based on assured or verified information, such as the Core BRSR.
4. Access to Investment from ESG Funds
According to a recent SEBI mandate, an ESG scheme must invest a minimum of 65% of its AUM in companies reporting on comprehensive BRSR and providing assurance on BRSR Core disclosures. This requirement will be applicable from October 01, 2024, onwards. ESG schemes that are not in compliance with the criteria cannot make fresh investments in companies without assurance on BRSR Core.
5. Reduces the Risk of Misreporting and Greenwashing
Assurance gives an independent perspective on ESG Reporting which helps in identifying and mitigating potential gaps in the process and reduces the risk of greenwashing.
6. Facilitates Visibility in the Supply Chain
SEBI has mandated the top 250 listed entities to provide ESG disclosures for their value chain from FY 2024-25, with limited assurance on the same applicable on a comply or explain basis from FY 2025-26. With increasing compliance requirements, these entities would prefer their value chain to align with their vision of sustainability and compliance. Undertaking BRSR assurance will boost confidence and help gain visibility and preference across the supply chain, facilitating reliance, transparency and trust.
Types of Assurance Frameworks Relevant to BRSR
The most prevalent types of Assurance Frameworks are as follows:
- International Standard on Assurance Engagements (ISAE) 3000 issued by International Auditing and Assurance Standards Board (IAASB).
- Standard on Sustainability Assurance Engagements (SSAE) 3000 and Standard on Assurance Engagements (SAE) 3410 Assurance Engagements on Greenhouse Gas Statements, issued by The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI).
- AA 1000 Assurance Standard
As per FAQs on BRSR Core released by SEBI in August 2023, the circular does not mandate or recommend the use of any specific assurance standard. However, disclosure should be made as per the assurance standard that is used.
Types of Assurance
There are two main categories of assurance. They are as below:
1. Internal Assurance or Agreed Upon Procedures (AUP)
It refers to processes, procedures and activities within an organization conducted by management or third-party consultants under the direction of management to provide confidence regarding the effectiveness of operations and the reliability of reporting. This can include internal audits, report validation, management reviews, control self-assessments and other activities aimed at evaluating and improving internal controls, risk management practices and governance processes.
2. External Assurance
It refers to evaluation and validation of an organization’s operations, processes and reporting by an independent third party to enhance credibility and confidence among stakeholders.
As per SSAE 3000, each external assurance engagement is classified as below:
Reasonable Assurance Engagement
- This is an examination engagement like Statutory Audit.
- In reasonable assurance, the practitioner reduces engagement risk to an acceptably low level by gathering sufficient and appropriate evidence to support their opinion.
- Here, the practitioner’s conclusion conveys their opinion on the outcome of the evaluation of the underlying subject matter against criteria.
- Reasonable assurance conclusions are framed positively, indicating that, based on the procedures performed, the management’s assertion regarding a specific subject is prepared. It has a broader scope compared to a Limited Assurance Engagement.
Limited assurance engagement
- This is a review engagement like Limited Review of quarterly results.
- The nature, timing, and extent of procedures performed in a limited assurance engagement is limited compared to reasonable assurance but is planned to obtain a level of assurance that in the practitioner’s professional judgment is meaningful.
- Limited assurance conclusions are expressed negatively, which means that based on the testing performed, there is no indication that the management’s assertion regarding a specific subject is incorrect.
In terms of confidence, the levels of assurance, from the lowest to the highest degree of confidence, are as follows:
- Internal Audits/Validation/Agreed upon procedures
- Limited Assurance
- Reasonable Assurance
- Absolute Assurance
How to Choose a Type of Assurance?
Reasonable assurance is more comprehensive and robust, as compared to limited assurance. Concerning greenwashing at the company level, SEBI has mandated reasonable assurance of BRSR Core disclosures for the top 150 listed entities for FY 2023-24.
Here is a simplified guide on selecting the type of assurance for your organization.
1. Entities Mandated by SEBI as per the Glide Path
Mandatory Reasonable Assurance must be obtained for BRSR Core attributes. For additional parameters of BRSR, you may opt for Validation or Voluntary Assurance (Limited or Reasonable) depending on the desired degree of assurance.
2. Other Entities
Considering the benefits that assurance has to offer, you can opt for Voluntary Assurance (Limited or Reasonable) based on the desired degree of assurance. Here, you can choose the scope and parameters for which you require assurance.
Alternatively, you can also consider having your BRSR Report validated by an external party. While not as rigorous as assurance, this process will help minimize the chances of clerical and arithmetic errors during data collection, consolidation and reporting. Additionally, this validation will prepare the entity for future BRSR Assurance.
How to Choose an Assurance Provider?
The internal assurance/validation provider can be selected at the discretion of the management in line with the company’s internal policies. However, as per SEBI mandate, below are a few points the entity must keep in mind while selecting an external assurance provider:
- Ensure that the assurance provider has the necessary expertise to undertake reasonable assurance.
- Ensure that there is no conflict of interest with the assurance provider. For instance, it must be ensured that the assurance provider or any of its associates do not sell their products or provide any non-audit/non-assurance-related services, including consulting services, to the listed entity or its group entities.
- Assurance activities, including third-party certifications, tax audits, system audits, and tax filings, may be performed by an assurance provider for the BRSR Core of a listed entity or its group entities. However, this is only allowed if the listed entity confirms that such activities do not present any conflicts of interest or compromise the independence of the assurance provider.
- Activities such as risk management, project management, consulting services, investment advisory services, investment banking services, design and implementation of information systems, rendering of outsourced financial services, actuarial services, accounting and bookkeeping services cannot be undertaken by an assurance provider for the listed entity or its group entities. It may be noted that this is an indicative and not an exhaustive list.
- Internal auditor of a listed entity or its group entities, cannot be appointed as the assurance provider.
- The statutory auditor of a listed entity can be appointed as the assurance provider.
How to Prepare for BRSR Assurance?
Bridging the gap from BRSR Reporting to BRSR Assurance involves a strategic transition to ensure the accuracy, credibility and reliability of sustainability disclosures.
Steps to Undertake to Bridge the Gap Between BRSR Reporting and BRSR Assurance
1. Understand Assurance Requirements
Conduct a thorough gap analysis to identify the disparities between your current BRSR reporting and the requirements for assurance. This will help identify the data available with the company and the focus areas for improvement.
2. Formalize ESG Charter
ESG charter is a document outlining the company’s values, goals, and specific strategies related to sustainability, social responsibility and governance. It serves as a guide for integrating ESG considerations into business operations and decision-making processes.
3. Formalize Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Create and maintain SOPs related to control environment, data collection, data analysis, BRSR Reporting Assumptions and Procedures relevant to the data points subject to assurance.
4. Internal Training
Provide training to internal teams involved in BRSR data collection and reporting process. Educate them on the requirements and set clear expectations for BRSR Assurance to align reporting practices.
5. Engage Assurance Providers
Identify and engage the internal and/or external assurance providers.
6. Refine Data Collection Processes
Strengthen data collection processes to ensure accuracy and reliability. Implement robust systems for in-house data verification, validation and documentation. This may also include using data collection tools for seamlessly capturing the data at the source and maintaining sufficient trail and evidence for audit.
7. Conduct Pre-Assurance Audits
Conduct internal audits, internal validation or pre-assurance checks to identify and address any potential issues before engaging external assurance providers. This step helps streamline the assurance process that can be implemented concurrently with the streamlining of the data collection and integration process.
8. Integrate Assurance into Reporting Cycle
Integrate the assurance process seamlessly into your reporting cycle. Ensure assurance activities are conducted promptly to align with reporting deadlines.
9. Continuous Improvement
Treat BRSR Assurance as an iterative process. Continuously evaluate and improve assurance practices based on feedback, changing standards, and organizational learning.
Conclusion
BRSR and its assurance transcend a mere checkbox exercise. It is a strategic leap towards a sustainable and responsible future. A well-executed BRSR implementation stands as a prerequisite for a smoother path through BRSR Assurance. However, it comes with its fair share of challenges too. From data accuracy issues to the dynamic nature of evolving standards, companies often struggle with complexities during the reporting and assurance process. But these challenges are not roadblocks, they can be opportunities to stand out.
Why Choose Incorp Advisory?
InCorp Advisory provides a complete ecosystem and support for your BRSR needs. Our team of experts conducts a 360-degree assessment to identify and highlight potential risks and opportunities which can arise with BRSR reporting. Our clients range from listed companies to investors as we assist them not only to improve their ESG reports but also help create valuable investments. To learn more about BRSR Reporting or ESG services, you can write to us at info@incorpadvisory.in or reach out to us at (+91) 77380 66622.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on BRSR Core Assurance
Yes, BRSR Core Assurance is mandatory for the listed entities specified by SEBI as per the glide path.
Not complying with BRSR Core Assurance may result in non-compliance with SEBI Listing Obligations and Disclosure Regulations (LODR), leading to penalties and other legal consequences.
No, the internal auditor of a listed entity or its group entities, cannot be appointed as the external assurance provider for the BRSR Core.
Yes, the statutory auditor of a listed entity can be appointed as the assurance provider for the BRSR Core.
No, it is not mandatory. You may opt for Limited or Reasonable Assurance for your BRSR depending on the desired degree of assurance. Alternatively, you can also consider having your BRSR Report validated by an external party. This validation will prepare the entity for future BRSR Assurance.
Share
Share