EU CSRD – What Should Businesses Know About the Framework?

EU CSRD – What Should Businesses Know About the Framework?
New ESG framework by EU called CSRD: A complete guide on the framework all businesses need to know.
- Authors
- Last Updated
- Tags
- Last Updated
- Tags
Share
Table of Contents
- Authors
- Last Updated
- Tags
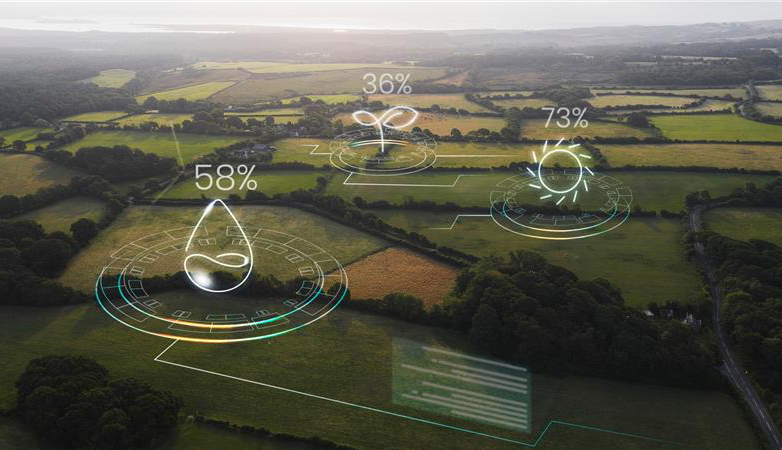
Many countries across the world have made it mandatory to have ESG compliance as per the regulations. Enterprises are not just judged by their financial health nowadays; clients and investors are increasingly interested in new sustainability compliances being introduced globally and testing businesses as per the frameworks. There are different frameworks that assess whether a company is compliant with all the ESG standards or not. One such framework is the new European Union (EU) Corporate Sustainable Reporting Directive (CSRD).
ESG frameworks are a set of parameters that help in reporting ESG initiatives adopted by any organization. There are three types of ESG frameworks, namely Regulatory, Voluntary and Benchmark frameworks. In regulatory frameworks, all the decided areas need to be addressed and it is generally regulated by a government body. In voluntary frameworks, organizations have the autonomy to choose the areas they want to address according to their industries and requirements. Thirdly, benchmark frameworks usually feature a questionnaire where every area needs to be addressed, and often, they also involve a scoring structure. EU CSRD is a regulatory framework introduced by the European Union. In this blog, we explore EU CSRD while highlighting the key aspects of the framework.
What is EU CSRD?
The European Union (EU) Corporate Sustainable Reporting Directive (CSRD) was introduced a few years ago. It builds on the existing Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD) introduced by the European Financial Reporting Advisory Group (EFRAG) in 2014. The NFRD helped in inducting a reporting practice that was not related to financials but ESG practices of an organization. In 2023, EU CSRD was introduced to regularize ESG reporting practices among corporations. CSRD focuses on double materiality of reports, including ESG information and financial information.
CSRD requires companies to report according to European Sustainability Reporting Standard (ESRS). It directs organizations to focus on double materiality, which includes ESG and financial elements. CSRD will transmute how the organizations report on ESG parameters. It will also incorporate companies that were previously not required to submit ESG reports under NFRD. EU CSRD is a directive that will standardize what to report and how to report for organizations.
What is ESRS?
European Sustainability Reporting Standard (ESRS) that complements EU CSRD was also introduced in 2023 by EFRAG. It specifies new reporting standards that cover a wider range of ESG parameters. It details how companies should report their ESG practices while complying with the EU CSRD. ESRS also highlights what to report in ESG reports. In short, ESRS provides a framework and methodology for reporting ESG practices. It has twelve standards comprising of two overarching standards (ESRS 1 and 2) and ten topical standards (ESRS E1 to E5, ESRS S1 to S4 and ESRS G1).
| ESRS 1 | General Requirements |
| ESRS 2 | General Disclosures |
| ESRS E1 | Climate Change |
| ESRS E2 | Pollution |
| ESRS E3 | Water and Marine Resources |
| ESRS E4 | Biodiversity and Ecosystems |
| ESRS E5 | Resource Use and Circular Economy |
| ESRS S1 | Own Workforce |
| ESRS S2 | Workers in the Value Chain |
| ESRS S3 | Affected Communities |
| ESRS S4 | Consumers and End-Users |
| ESRS G1 | Business Conduct |
What is the Difference Between EU CSRD and ESRS?
EU CSRD and ESRS are complementary mechanisms that go hand-in-hand. While CSRD sets regulations and directory of what needs to be addressed, ESRS sets out the reporting method and framework through which the reports can be compliant with the CSRD. For example, imagine there is a job vacancy at a company, ESRS would represent the job requirements while CSRD would be the company mandating them.
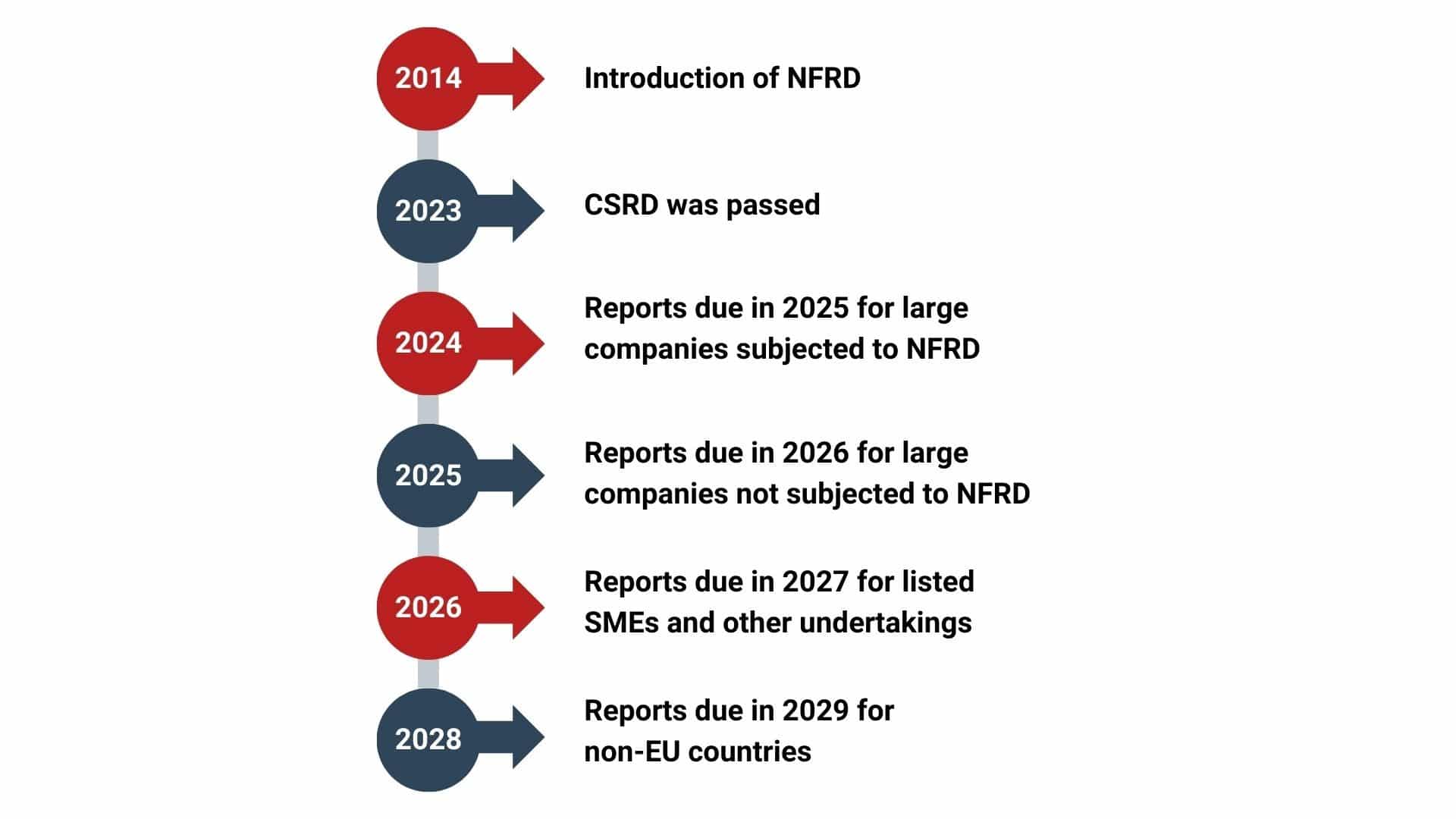
Timeline of EU CSRD
EU CSRD came into being on 5th of January 2023. Companies that were a part of NFRD need to publish their reports for the financial year 2024 in the next year i.e. 2025. Large companies not under NFRD, SMEs and non-EU companies need to submit the reports in 2026, 2027 and 2029 respectively.
Advantages of EU CSRD
Standardization in Reporting
With CSRD standardizing reporting parameters it becomes easy to compare ESG practices of one company with another.
Compliance with Global standards
The new EU CSRD is in line with the other ESG standards like Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) that are already in place. This would help in establishing a global standard for ESG reporting practice.
Increase in Transparency
With increased transparency, stakeholders, investors and clients would be able to access and evaluate the information.
Who has to comply?
Around 50,000+ companies are estimated to be covered under the new EU CSRD regulations. It includes the below:
- Companies under NFRD (Around 11,700 companies)
- Listed SMEs
- Large companies
- Third country businesses with net turnover of over $160 million in Europe and companies who have subsidiaries/branches in European Economic Area (EEA) that generate over €40 Million.
Steps for Businesses
We realize it can be difficult to navigate through ESG regulations given the recency of the field and ever-changing regulations. Here are some steps that businesses can follow:
- Realizing whether the company is subject to the new CSRD eligibility.
- Identifying current sustainability practices and gaps in the current ESG practices.
- Developing a reporting strategy after identifying gaps. The report should comply with the new CSRD regulations and the ESRS reporting requirements.
- Implementing the most suitable reporting processes and procedures.
- Keeping update of new developments regarding ESRS reporting standards.
Conclusion
The EU CSRD aligns with the latest global ESG standards and has also introduced the ESRS. Both CSRD and ESRS together can ensure a standardized parameter, method and process for reporting sustainability practices in organizations worldwide. Sustainability reporting is a small step into what the future holds for corporations. Many such frameworks and bodies are expected to be introduced soon. Hence, the need for ESG solutions has also become ever-so-relevant.
Why Choose InCorp Global?
We help businesses with incorporation and adoption of ESG practices. InCorp consists of qualified individuals trained in Social Impact Assessment. Our team has experience in delivering solutions across various industries. Apart from ESG, we also offer a range of services along different verticals. We can be a one-stop solution for all your business needs. To learn more about EU CSRD Reporting and other ESG services, write to us at info@incorpadvisory.in or reach out to us at (+91) 7738066622.
Frequently Asked Questions
EU CSRD was introduced on January 5, 2023, and the first report was published in 2025.
Yes, EU CSRD applies to organizations from countries outside EU doing business in the European Economic Area (EEA). Third country businesses with net turnover of over €150 million in Europe and companies who have subsidiaries/branches in EEA generating over €40 million.
There are three types of ESG frameworks, namely Regulatory, Voluntary and Benchmark frameworks. GRI, TCFD, EU CSRD, CBAM, etc. are some examples of ESG frameworks.
The first report for the financial year 2024 will be published by the companies under NFRD, henceforth publishing them in 2025. Large companies not under NFRD, SMEs and non-EU companies need to submit reports in 2026, 2027 and 2029 respectively.
Third countries are nations that are not a part of the European Union. Citizens from these countries cannot avail themselves of the rights that are associated with the EU.
Share
Share