How to Choose Right ESG Reporting Framework for Business

How to Choose Right ESG Reporting Framework for Business
Navigate ESG frameworks with ease: Key factors to consider for selecting the best reporting standard for your business's goals and stakeholder needs
- Last Updated
UNGC defines corporate sustainability as “Corporate sustainability is a company’s delivery of long-term value in financial, environmental, social, and ethical terms.”
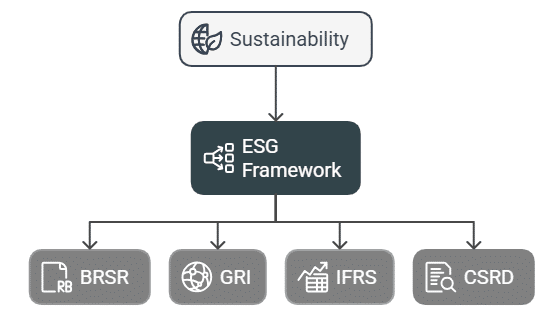
While sustainability is a broad concept and helps companies to set up strategic vision, ESG frameworks help organizations to define methodologies, set ESG metrics and publish transparent and comparative reporting. ESG Frameworks have become a crucial standard for assessing a company’s overall performance. Investors and clients specifically focus on sustainability reports prepared using the ESG standard frameworks to evaluate a company.
Many countries have made it mandatory for businesses to report their sustainability practices and outcomes based on a defined ESG framework. For ESG reporting, there are several frameworks, standards, and ESG ratings that an organization can use as per the requirements of their industry and geographic locations.
In this blog, we will take you through ESG reporting frameworks, ESG standards, and ESG ratings. It provides details on reporting frameworks and standards while choosing the right reporting mechanism for your organization.
ESG Reporting Frameworks/Standards/Disclosures
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI)
GRI is an independent body headquartered in Amsterdam. It is one of the most used and followed ESG reporting standards worldwide. GRI covers a range of ESG parameters that can be tailored to the organization’s needs. The sustainability reports can be ‘in adherence to’ the GRI or ‘in reference to’ the GRI. The new version of GRI Standards 2021 became mandatory from January 1, 2023. GRI also started publishing sector standards. Recently, GRI released its new mining sector standard and a new topic standard covering biodiversity. GRI also released a draft framework covering climate change.
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
The International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) is an independent standard-setting organization under the IFRS Foundation aimed at developing and approving IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards. IFRS has published S1 and S2 frameworks by combining features of existing sustainability reporting frameworks including SASB, TCFD and Integrated Reporting. S1 and S2 frameworks were issued in June 2023 and made effective starting January 2024. With several countries planning to adopt the IFRS sustainability framework, ISSB has launched a new roadmap tool to help jurisdictions adopt the IFRS framework. Brazil was the first country to adopt the IFRS S1 and S2 framework. As of the end of 2024, 13 jurisdictions have already adopted IFRS frameworks.
Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB)
SASB is a sustainability reporting framework that focuses more on the financial side of ESG initiatives. SASB sets sustainability accounting standards that help public companies disclose material and decision-influencing information to investors. SASB Standards help organizations to provide industry-specific disclosures. On average, each standard has 6 disclosure topics and covers 13 ESG metrics. These can be consistently applied to organizations operating in similar industries. SASB standards have a strong connection with other reporting and rating frameworks. ISSB has stated that in the absence of specific IFRS Sustainability disclosure standards, companies can use SASB to define the matrices required to be disclosed as per IFRS S1 and S2.
Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD)
The CSRD and European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) are key components of the EU’s Sustainability reporting framework created by The European Financial Reporting Advisory Group (EFRAG). EU CSRD is a new ESG framework created to cover wider ESG factors like GHG and double materiality. To implement CSRD, ESMS was implemented which has 12 sustainability reporting standards. The EUCSRD is a regulatory mandate that requires companies to submit ESG reports. To ensure compliance, companies must adhere to the ESRS, which serves as the prescribed reporting framework under the CSRD.
Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)
TCFD is a reporting framework for disclosing climate-related risks and opportunities for an organization. Investors can gain consistent and comparable data about risks and opportunities along with their financial impacts.
Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report (BRSR)
BRSR is an example of a regional sustainability reporting framework applicable only in India. While in the process of harmonising ESG reporting within the country, several countries like India, Hong Kong, etc instead of directly mandating a global ESG Framework, adopted a regional ESG Reporting requirement. BRSR is mandated by Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) to top 1000 listed companies of the country by market cap.
Sustainability Tracking, Assessment & Rating System (STAR) Framework:
The STAR framework was developed by Association for the Advancement of Sustainability in Higher Education (AASHE). STAR is an example of an industry specific framework usually adopted by colleges and university to measure and report on their sustainability performance. It is a combined reporting and ESG rating framework allowing institutions to report and track their rating.
Benefits of ESG Frameworks
ESG frameworks not only increase the transparency and accountability of an organization, but there are numerous benefits of, which some are listed below:
Risk Management
ESG frameworks often include the need for companies to assess risks and opportunities. Identifying these risks and opportunities aids an organization to adopt risk management techniques and opportunity maximization techniques.
Standardization
ESG framework helps organizations to track and monitor the ESG matrices standard to the industry or the region organization operates. This helps the organization to track and compare progress with other organizations operating in the same industry. This enables companies to define meaningful goals and targets.
Brand Value
Sustainability reporting enhances the brand value of any organization. The organization appears more responsible to investors, who prefer not to be attached to any controversial practices. ESG reporting helps companies build their brand reputation among all stakeholders.
Innovation
Mitigating ESG risks and maximizing ESG opportunities lead to innovation and new techniques coming into specific industries. Many cost-efficient and more productive operations might emerge out of ESG initiatives.
Stakeholder Relations
One of the major benefits of ESG reporting is that it improves the stakeholder’s relationship with the given organization. The organizations producing ESG reports can establish a communication model with the stakeholders from which they all benefit.
Challenges of Adopting an ESG Framework
As mentioned above, there are numerous benefits of adopting an ESG reporting practice. The challenges associated with certain frameworks might differ from one another. However, there are some common challenges that organizations may face while adopting ESG frameworks and practices.
Some of the challenges include:
No universal framework
There is no universal framework that is accepted everywhere, as it leads to non-comparable reports when the reports are aligned to different frameworks. Also, it becomes challenging for organizations to choose the right framework. Hence, quite some background research goes into choosing the correct ESG reporting framework for your organization.
Short-term cost
The short-term cost of ESG reporting practices might increase the cost of operations. However, there are a lot of long-term benefits that can be availed by adopting a regular sustainability reporting practice.
Time Efficiency
The process of choosing a framework and developing an ESG report may be time-consuming. However, time efficiency is likely to increase with regular ESG reporting.
Selecting the Right ESG Reporting Framework or Standard
Selecting the right ESG reporting framework is crucial in utilizing ESG opportunities and mitigating risks fully. It is vital to understand the requirements and needs of the organization to adopt an out-and-out strategy and ESG reporting framework.
While choosing the ESG Reporting framework, the following has to be followed:
1. Industry
The industry in which your company functions is one of the distinctive factors. It helps in choosing the right ESG reporting framework. For example, a manufacturing company will have to adopt different mechanisms and ESG reporting frameworks than a service-oriented company.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Many national and international compliance regulations have been developed to promote ESG practices. While choosing the ESG reporting framework, you should check regulatory requirements as per your geographical area, too.
3. ESG Priorities
Different ESG reporting frameworks cover different areas of ESG. Make sure to select a framework that is in coherence with the ESG goals and parameters of your company.
4. Stakeholders
Stakeholders should be consulted, no matter the ESG reporting framework you choose. Make sure to develop a good feedback loop in your communication model. Stakeholder priority can help you select the framework better while addressing the issues at hand.
5. Ease of Implementation
It is important to consider the ease of implementation of the ESG reporting framework. You should consider your organization’s ability to assess and report on the required parameters.
Steps in ESG Reporting
Since ESG is a new phenomenon, there is a lot of ambiguity around the ESG reporting frameworks and procedures. It can often be confusing for entities starting their sustainability reporting journey.
Here is a step-by-step guide to navigate during ESG reporting:
- Define your company’s priorities
- Allocate the responsibility of sustainability reporting
- Identify the priority areas
- Understand and determine your data requirements
- Set systems for data collection
- Report your sustainability progress
- Build credibility in your report through external assurance
To further understand the steps involved in ESG reporting, you can visit this blog.
Conclusion
There is no denying the importance of ESG reporting frameworks in ensuring effective and comprehensive sustainability reporting. The right framework can bring exponential returns. As a responsible organization, it is crucial to have an ESG reporting mechanism in place.
Why Choose InCorp Global?
At InCorp, we feature a team of ESG experts who are well-qualified to help you understand your sustainability reporting processes in adherence with various leading frameworks like GRI, TCFD, IFRS, EcoVadis, MSCI, S&P, EU CSRD, GRESB, and more. We also offer services to improve your sustainability disclosures, rating scores, gaps in sustainability reporting, and more. If you have any questions or require assistance regarding our process, please write to us at info@incorpadvisory.in or reach out to us at (+91) 77380 66622.
Authored by:
Muskaan Jain | Sustainability & ESG
FAQs
ESG reporting is a mechanism through which an organization discloses its sustainability practices and their outcomes. Generally, the reporting is done through reports which are produced annually.
Yes, there are regulations by national and international bodies that govern ESG reporting. It may vary based on the size of your company and geographic location. It is important to stay updated on the new regulations that are relevant to your company.
Third-party assurances are very important in ESG reporting. Mostly because they provide an external quality check and increase the reliability of the sustainability report.
There is no mandate for linking your ESG reports with SDGs. However, the nature of SDGs and ESG initiatives is highly interlinked. ESG initiatives can be aligned with SDGs and the outcomes can be produced in the progress made towards SDGs in the annual sustainability reports.
Share
Share