Introduction to BRSR Compliance: A SEBI Mandate

Introduction to BRSR Compliance: A SEBI Mandate
Understand the BRSR reporting compliance for your company, its advantages, and recent developments in the BRSR framework.
- Authors
- Last Updated
- Tags
- Last Updated
- Authors
- Last Updated
- Tags
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) introduced BRSR in 2021 and mandated India’s top 1000 listed companies (by Market Capitalisation) to submit the BRSR reports from FY 2022-23 onwards with FY 2021-22 being a voluntary year. In the FY 2022-23, Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) gained momentum in India, with the top 1000 listed companies publishing their BRSR reports. Following this, many companies, including non-listed companies, were observed voluntarily publishing their sustainability reports. We are now entering the second leg of this mandatory phase in FY 2023-24 with SEBI introducing amendments for companies to make BRSR reporting more exhaustive. In this blog, we look at the significance of sustainability reporting, BRSR compliance, its evolution in India, advantages of BRSR, recent amendments, and its future.
What is the Significance of Sustainability Reporting?
Sustainability reporting presents a holistic picture of a company’s operation and position along with its financial reporting as the risks associated with environmental, social and governance aspects are captured in the form of well-defined metrics. These metrics give a clearer picture of where the company stands in its shift toward sustainability. In the recent past, many institutions and authorities like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), the European Union (EU) and The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) across the globe have been promoting sustainability reporting and making regulatory changes due to the challenges of climate change and environmental issues on a global scale.
A significant push for making sustainability reporting mainstream has been observed. Regulators worldwide are seen actively pushing companies to adopt responsible and sustainable business practices. These regulatory changes are accelerating and increasing in number and complexity over time. Beyond environmental concerns, there has also been a shift in the perception of investors toward sustainability. They are seen taking an active interest in the companies that are conducting their businesses responsibly and sustainably.
Evolution of Sustainability Reporting in India
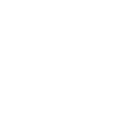
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs initiated efforts towards sustainability in 2009 by issuing the National Voluntary Guidelines on Corporate Social Responsibility. Later, SEBI became the torchbearer for promoting sustainability reporting in India. In 2012, SEBI mandated top 100 listed companies by market capitalization to furnish BRR along with their annual reports. Later, BRR (based on NVGs) was replaced with BRSR (based on NGRBCs) after significant improvements in the former for more comprehensive and in-depth disclosures for company operations.
Timeline of Sustainability Reporting Evolution in India
What is BRSR?
BRSR is a standardized reporting framework format for companies to disclose their ESG performance. It is created in alignment with many global frameworks like GRI, TCFD, SASB, etc. It has solved a significant challenge by bringing a format of uniformity for all the investors to evaluate Indian companies and benchmark their performance. BRSR structure is based on the National Guidelines on Responsible Business Conduct (NGRBC) developed by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
NGRBC guidelines were made to encourage businesses to adopt responsible and ethical practices that align with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It includes various aspects like responsible business conduct, including ethical behaviour, stakeholder rights, human rights, environmental protection, workers’ rights, consumer protection, and anti-corruption measures. It is an excellent tool for companies to align their business performance with NGBRC principles.
It helps companies to integrate non-financial parameters in their decision making. Moreover, it incorporates Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) from international frameworks, aligning them with global reporting trends. In addition, the information presented in the BRSR is relevant for a broad group of stakeholders, ranging from investors, shareholders, bankers, employees, community members, regulators, customers, and suppliers.
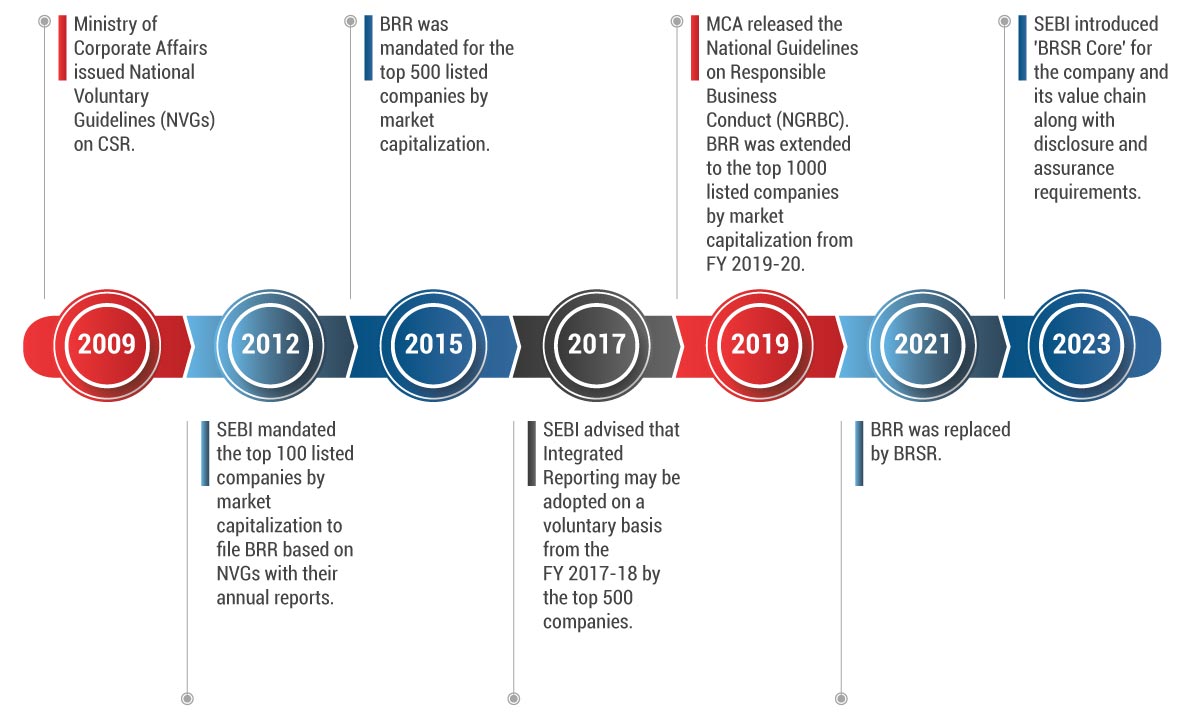
Structure of BRSR
The reporting format of BRSR consists of three sections: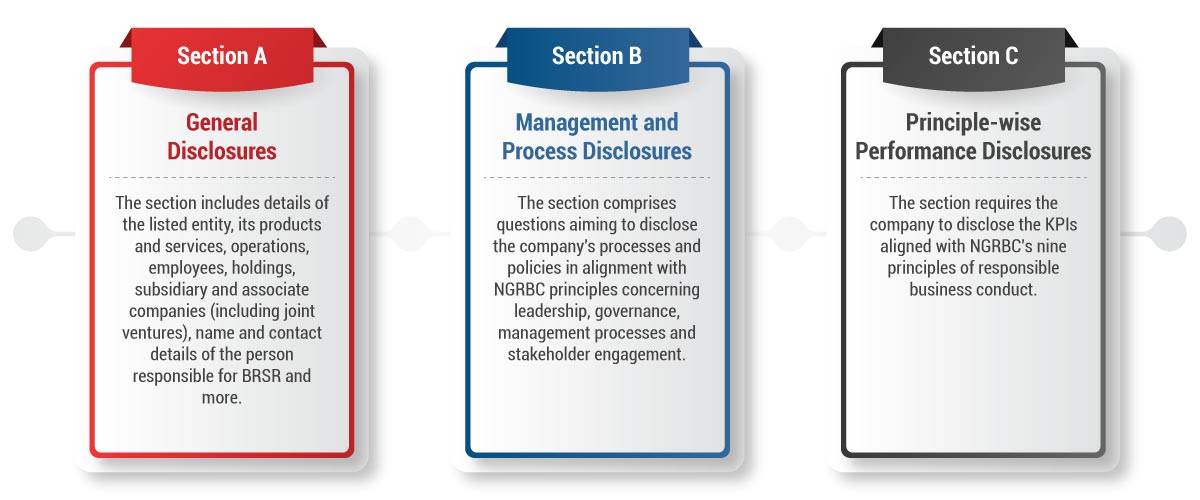
In BRSR, Section A and Section B are mandatory while under Section C, companies are required to report information based on two categories including leadership and essential indicators. Every company must disclose information under ‘Essential Indicators’ while companies can voluntarily choose to disclose the information under ‘Leadership Indicators’. Disclosing information on ‘Essential Indicators’ is the minimum obligation for companies to meet the BRSR reporting criteria outlined in the framework.
Principles of BRSR
The below table demonstrates the alignment between BRSR principles and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. 
Formats of BRSR
According to the guidelines recommended by MCA established Committee on Business Responsibility Reporting (BRR), there are two-format approaches – Comprehensive BRSR and BRSR Lite. The BRSR Lite has less disclosures as compared to Comprehensive BRSR. BRSR Lite format has been developed for non-listed companies below a certain threshold (currently undefined by SEBI). These companies can adopt a ‘lite version’ of the BRSR format voluntarily. The driving force behind this initiative is to equip smaller companies with the readiness and knowledge to report on ESG-related matters. Comprehensive BRSR may be extended to several unlisted companies that meet specified thresholds of turnover and/or paid-up capital.
Advantages of BRSR
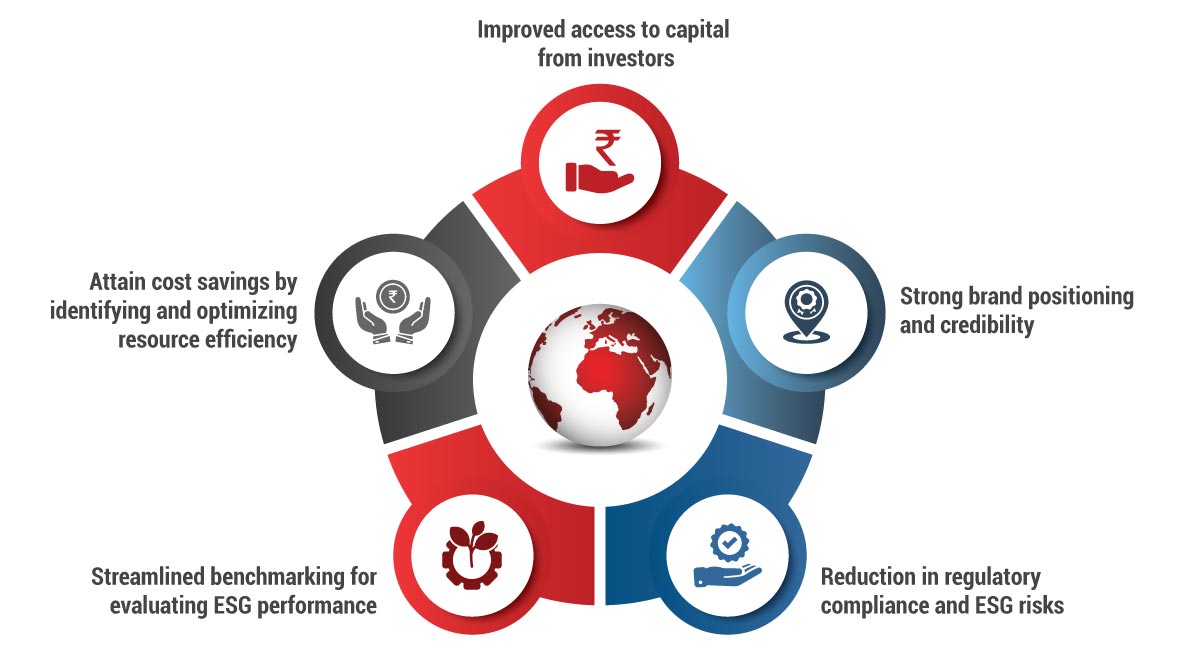
Recent Amendments in the BRSR Framework
Amid increasing concerns about the activities of ESG rating providers (ERPs), which may lead to bigger concerns like investor protection, market efficiency, risk pricing, capital allocation, and greenwashing, SEBI introduced the ‘BRSR Core’ on 12 July 2023. The circular can be accessed here.
SEBI revised the BRSR framework to introduce the ‘BRSR Core’ as a subset of the BRSR including attributes relevant to the evolving unique context of the Indian/Emerging markets. These include job creation in small towns, openness of business, gross wages paid to women, etc. which are relevant to Indian markets.
From FY 2023-24, the top 1000 listed entities (by market capitalization) are required to make disclosures as per the updated BRSR format within the Annual Reports. A glide path has also been specified for the listed companies to undertake reasonable assurance of the BRSR Core. In FY 2023-24, the top 150 listed companies by market capitalization are required to undertake ‘reasonable assurance’.
SEBI’s advisory committee on ESG issues recommended that ESG rating providers should be permitted to provide a Core ESG rating based on indicators that are assured while providing comments or outlook on unverified or unassured data.
In addition, BRSR Core disclosures account value chain for comprehensive evaluation in sustainability reporting to offer a holistic view of a company’s ESG performance. This is an excellent move to extend the scope of responsible business practices from its boundaries to the value chain. This can address potential ESG risks in companies’ value chains that may arise from outsourcing activities. To learn more about the BRSR Core, click here.
Future of BRSR Compliance in India
India’s BRSR framework is a great reporting format that is at par with international frameworks. Also, the trajectory of BRSR reporting looks promising with SEBI making continuous efforts to mainstream sustainability reporting in India. Many companies have started realizing the significance of sustainability, even though it started as compliance.
Small-listed companies are also reporting their sustainability performance amid growing consciousness for sustainability. They are allowed a significant timeframe to adapt as the applicability is as per the glide path. Meanwhile, SEBI has been working to combat greenwashing and emerging loopholes by amending the BRSR framework. For comprehensive BRSR reporting, including value chain disclosures is a significant step.
With new developments, companies need to stay vigilant and track all the regulatory changes pertaining to BRSR compliance. Companies must improve their data collection tools and internal systems to use BRSR as an effective tool. Internal teams should engage often as data collection requires great coordination. It is also essential for them to understand the BRSR reporting requirements. ESG training needs to be conducted within companies to increase awareness. Staying proactive and adaptable is critical for companies seeking to excel in sustainable reporting and navigating the evolving regulatory landscapes effectively.
Why Choose InCorp Advisory?
We understand that BRSR Reporting can be a complex task for your company. Our team has in-depth experience in handling BRSR reporting requirements and projects for businesses across various sectors and stages. To learn more about BRSR Reporting or ESG services, you can write to us at info@incorpadvisory.in or reach out to us at (+91) 77380 66622.
FAQs
Having garnered funds from the public, listed companies bear a consequential element of public interest. Furthermore, they are obligated to furnish exhaustive disclosures on a routine basis.
Companies are advised to cultivate a comprehensive understanding of the disclosures delineated in the BRSR framework. Concurrently, they should establish meticulous processes for accurate data collection or consider collaboration with professionals possessing the requisite expertise to navigate the regulatory landscape effectively.
BRSR compliance is mandatory for the top 1000 listed companies in India. Even if a company has produced an Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) report conforming to international standards, submission of the report to the SEBI in the prescribed BRSR format is obligatory. However, the BRSR allows for cross-referencing with other documents prepared in alignment with diverse ESG standards.
Presently, companies are mandated to submit their BRSR in both extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL) and Portable Document Format (PDF).
BRSR Core incorporates KPIs for comprehensive disclosures, while certain KPIs from BRSR Comprehensive have transitioned from leadership to essential indicators. In summary, the BRSR Comprehensive format has undergone an update to integrate BRSR Core.
Share
Share