Simplifying KYC: Highlights of IFSCA’s KRA Regulations, 2025

Simplifying KYC: Highlights of IFSCA’s KRA Regulations, 2025
Explore the IFSCA’s KRA Regulations 2025
- Last Updated
Before IFSCA was established, multiple domestic regulators such as the RBI, SEBI, IRDAI, and PFRDA independently governed entities operating in the IFSC. However, there was a need for a streamlined and efficient regulatory framework. This led to the creation of IFSCA, to support growing businesses and provide ease of doing business in GIFT City. IFSCA was then notified as the unified regulator. The responsibility given was to oversee the development and regulation of financial products, services, and institutions within the International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) in GIFT City, Gandhinagar.
A key area of focus under the IFSCA framework was the Know Your Customer (KYC) process, a fundamental compliance requirement in the financial sector. Institutions are mandated to verify the identity and address of their customers to help prevent financial fraud, money laundering, and terrorist financing. This standardized KYC process not only reinforces adherence to Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CFT) guidelines but also enhances the overall integrity and security of the financial system.
In this context, the International Financial Services Centres Authority introduced the KYC Registration Agency (KRA) Regulations, 2025 to govern the functioning of KRAs within the IFSC. These regulations aim to ensure consistency in KYC practices, promote transparency and accountability, and facilitate real-time data availability. This ultimately contributes to better system standardization and regulatory oversight.
Legal Structure
The organizations ready to register as KRA shall establish:
- A Company
- 100% subsidiary of a stock exchange regulated in India, in the IFSC or in a Foreign Jurisdiction
- 100% subsidiary of a depository regulated in India, in the IFSC or in a Foreign Jurisdiction
- 100% subsidiary or branch of an entity engaged in activities of a similar nature as a KRA and regulated by SEBI or regulated in a Foreign Jurisdiction
Key Requirements for KRA setup
- Appointment of a Principal Officer and a Compliance Officer who shall have the minimum educational qualifications as required by regulations.
- Registered entity (KRA), Principal Officer, Key Managerial Persons and Shareholders will be required to comply with fit and proper requirements as specified in the regulation.
- Maintain Net Worth of USD 1 Million at all times.
- Maintain acceptable financial creditworthiness.
- Maintain necessary infrastructure such as office space, manpower, etc.
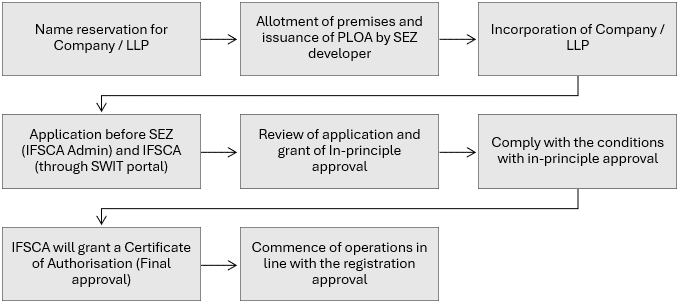
Process flow for Establishment in GIFT IFSC
Functions and Responsibilities of KRAs
| Category | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Core Responsibilities |
|
| Reporting Obligations |
|
| Obligations of Regulated Entities |
|
Additional Requirements for KRA
- The entity shall comply with the code of conduct.
- Keep books of accounts for at least 8 years.
- Intimation to the authority in case of material change in the information already furnished to the authority.
- Shall have suitable policy for redressal of grievances of customers and keep proper records of grievances.
- The entity shall have its accounts audited every year and furnish the report to IFSCA within 30th September of the following year.
Regulatory Fees
- IFSCA Fees -To be notified by IFSCA
- SEZ Fees
| Particulars | Amount (in INR) |
|---|---|
| Application Fees (one-time) | 5,000 |
| Registration fees (one-time) | 25,000 |
| Recurring fees (Annual) | 5,000 |
Conclusion
Being a registered KRA places an organization at the vanguard of digital trust and financial transparency as well as meeting regulatory mandates. It enhances the ability to manage risk better, provides real-time, verified customer information, and facilitates easier collaboration between financial institutions. The KRA model in GIFT IFSC is a forward-looking business edge for firms willing to invest in good governance, infrastructure, and compliance.
Authored by:
Kunj Solanki | GIFT City Services
FAQ
Regulated entities have an obligation to:
- Upload and finalize KYC information within 3 working days.
- Maintain physical copies of KYC documents.
- Not utilize KYC information for any unauthorized commercial purpose.
KRAs need to keep books of accounts, documents and records of KYC for a minimum of 5 to 8 years, depending on the type of record.
Yes, KRAs need to comply to a Code of Conduct that ensures:
- Integrity, transparency, and ethical business practices.
- Confidential handling of client information.
- Prompt redressal of complaints.
- No misrepresentations.
Non-compliance can result in:
- IFSCA inspection.
- Suspension or cancellation of registration.
- Other legal or disciplinary measures.
IFSCA appoints an Inspecting Authority to inspect books, infrastructure, policies, and operations of KRAs. KRAs must facilitate full cooperation and access in the event of such inspections.
KRAs may provide access to their systems to other financial sector regulators or authorised central KYC registries, with customer consent and applicable law.
Yes, KRAs shall:
- Implement an effective grievance redressal mechanism.
- Maintain records of complaints and their disposal.
- Comply with standards defined by IFSCA.
Share
Share