Initiatives in India’s Steel Industry: The Growing Green Transition

Initiatives in India’s Steel Industry: The Growing Green Transition
Sustainability initiatives in Steel Industry: Technologies adopted, key achievements, initiatives for green steel transition and the way ahead
- Last Updated
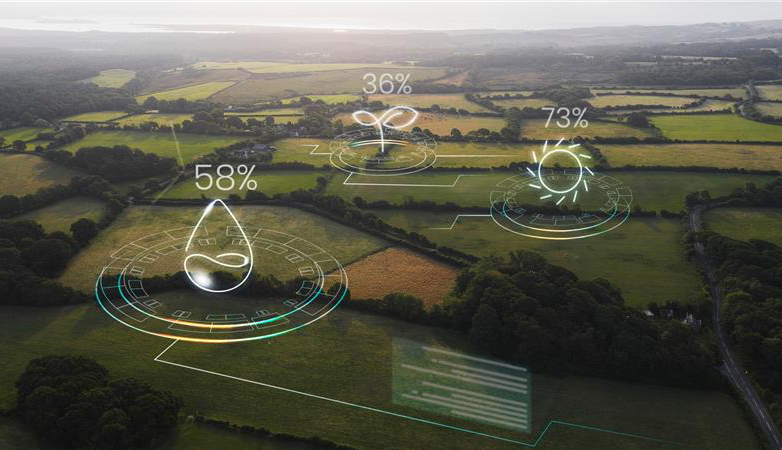
Steel, the world’s most important construction material is used in every aspect of our everyday life. While it is known for its great durability. Manufacturing steel accounts for approximately 8% of carbon dioxide emissions globally. Additionally, considering the size and significance of the steel industry, it is no surprise that steelmakers have been under pressure to accelerate their efforts to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). In keeping with the Indian government’s COP26 commitments, the Ministry of Steel (MoS) has invited stakeholders to prepare an action plan targeting the reduction of emissions in the steel industry. The industry accounts for 12% of total national CO2 emissions in India. In this blog, we take a look at the ESG initiatives in the Indian steel industry and key achievements by some known companies.
Initiatives for Green Steel Transition in India’s Steel Industry
Discussions were held recently on the current situation and the way forward for supporting the transition to green steel and adopting the latest technology the steel industry can use to facilitate this transition. Through different programs and regulations, the MoS has assisted steel plants in reducing energy use and pollution emissions. Some of the steps taken are listed below:
- Charter on Corporate Responsibility for Environment Protection (CREP)
- National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC)
- NEDO Model Projects for Energy Efficiency Improvement
- Iron & Steel Slag Utilization
According to a report by the MoS, energy consumption is generally high in most integrated steel facilities in India, ranging from 6-6.5 Giga calories per tonne of crude steel as compared to 4.5-5.0 steel plants in countries overseas. In keeping with the government of India’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), the Ministry of Steel has submitted NDCs to the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MOEF&CC) for the iron and steel sector to minimize GHG emissions by implementing clean and green technology. The Steel Association of India (SAI) recently compiled a list of policy enablers that might help advance green steel in the country. It includes preferential public buying of green steel, creating green steel standards, and other initiatives.
Key Achievements of the Iron and Steel Industry in India
- The steel industry has implemented cutting-edge clean technologies, improved the quality of raw materials, increased fuel economy, and created a carbon sink.
- The following are some of the best available technologies adopted by the Indian steel industry to improve energy efficiency and reduce GHG emissions:
| Technologies Adopted by the Steel Industry |
|---|
| Coke Dry Quenching (CDQ) |
| Sinter Plant Heat Recovery |
| Bell Less Top Equipment (BLT) |
| Top Pressure Recovery Turbine (TRT) |
| Pulverized Coal Injection (PCI) system |
| Dry-type Gas Cleaning Plant (GCP) |
| Cast House/ Stock House Dedusting System |
| Energy Monitoring & Management System |
| Secondary Fume Extraction System |
| Regenerative Burners in Re-heating Furnaces of Rolling Mills |
| Direct Rolling Process eliminating the need for Re-heating furnaces |
| Near Net Shape casting |
| Variable Voltage Variable Frequency (VVVF) Drives |
As a result of the implementation of the above measures, the specific CO2 emissions have significantly reduced from 3.1 T/tcs in 2005 to 2.5 T/tcs in 2020. In line with the efforts at the MoS, well known steel manufacturers have also taken significant steps and targets to contribute to the achievement of India’s NDCs.
As per their ESG report for FY 2020-2021, JSW Steel reduced its absolute Scope 1 & 2 GHG emissions by 7.4% last year while achieving a 3% energy intensity reduction across the organization. The company also achieved a 51% reduction in specific dust emissions generated from process stacks and reported a remarkable 7.3% reduction in water consumption. Prabodha Acharya, Chief Sustainability Officer JSW Group, said, “We have invested in gas-based power plants to utilize waste gases generated from steel operations, thereby reducing coal consumption. JSW also has steam generation from waste heat recovery at sinter plants”.
Paving the Way for Carbon Neutrality
Hindalco Industries has committed to achieving net carbon neutrality by 2050. Vedanta Ltd. is investing in green businesses to leverage green hydrogen, green metals, renewables, recycling, etc. The company stated in its September quarter results that Vedanta has set up the world’s first ESG Academy for capacity-building within the organization.
Companies with access to worldwide standards and technology, such as AM/NS, intend to get power for their upcoming expansions from renewable sources. Tata Steel is investing in CCU/S to capture and use carbon at the emission source in their blast furnaces and is moving steadily towards carbon neutrality. The company intends to become water-neutral at all its locations by 2030 and a zero-effluent organization by 2025.
Jindal Steel and Power Ltd.’s ESG targets include being one of the world’s top 10 lowest CO2-emitting steel businesses. The company intends to cut its carbon footprint by nearly half.
Conclusion
Steelmakers have made significant progress towards some SDGs, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving energy efficiency. However, there is still much work to be done. The buyers and customers of the steel industry are now demanding clean products. One of the key difficulties confronting the Indian steel industry is the country’s heavy reliance on coal in various steelmaking processes. Additionally, the industry is still reliant on dated and inefficient technology. As India strives to attain net-zero emissions by 2070 and steel production continues to grow, steelmakers must redouble their efforts to support the government’s decarbonization initiatives for a greener future.
Why Choose InCorp Global?
InCorp offers guidance to businesses at different stages across diverse sectors. Our team of experts have in-depth experience in managing the complexities and intricacies of ESG and BRSR practices. To learn more about our services, you can write to us at info@incorpadvisory.in or reach out to us at (+91) 77380 66622.
Authored by:
Aanchal Mathur | Sustainability & ESG
FAQs
The Indian steel industry is a significant contributor to carbon emissions and is under pressure to align with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The Ministry of Steel (MoS) has initiated actions to reduce emissions, accounting for 12% of India’s total CO2 emissions. Ministry of Steel is committed to a Net-Zero target by 2070.
Ministry of Steel (Mos) has introduced programs like the Charter on Corporate Responsibility for Environment Protection (CREP), the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) and the National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM). It aims to reduce energy use and pollution emissions in steel plants.
The industry has implemented cutting-edge technologies such as Coke Dry Quenching, Sinter Plant Heat Recovery and more. These measures have significantly resulted in a reduction in specific CO2 emissions.
The Charter on Corporate Responsibility for Environment Protection (CREP) is essential in guiding the Indian steel industry towards enhanced environmental sustainability. The Charter has set targets for conservation of water, energy, recovery of chemicals, reduction in pollution, elimination of toxic pollutants, management of residues that are required to be disposed off in an environmentally sound manner. The Charter has listed the action points for pollution control for various categories of highly polluting industries.
The National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) provides a comprehensive roadmap for India's efforts in addressing climate change challenges outlining strategic initiatives and policies across various sectors.
Share
Share