ESOPs for Indian Startups: A Preferred Tool for Hiring Talent

ESOPs for Indian Startups: A Preferred Tool for Hiring Talent
Leveraging ESOPs in Indian startups: Guide on the strategy for effective talent acquisition and retention
- Last Updated
Employee Stock Option Plans (ESOP), is a widely adopted methodology used by modern startups, notably established in Silicon Valley by companies like Google and Facebook during their initial stages. The success of this strategy has been mirrored in the Indian market by companies like Flipkart, Citrus Pay, and many other startups. When these startups made profits, many of their employees benefitted financially with some even becoming multi-millionaires. ESOPs play an important role in attracting and retaining talent for startups. Below are some of the leading unicorns in India whose ESOP pool have helped demonstrate their commitment to employee engagement and driven an excellent work culture.
ESOP Pool of Top Unicorn Start-ups in India (Amount in Crores)
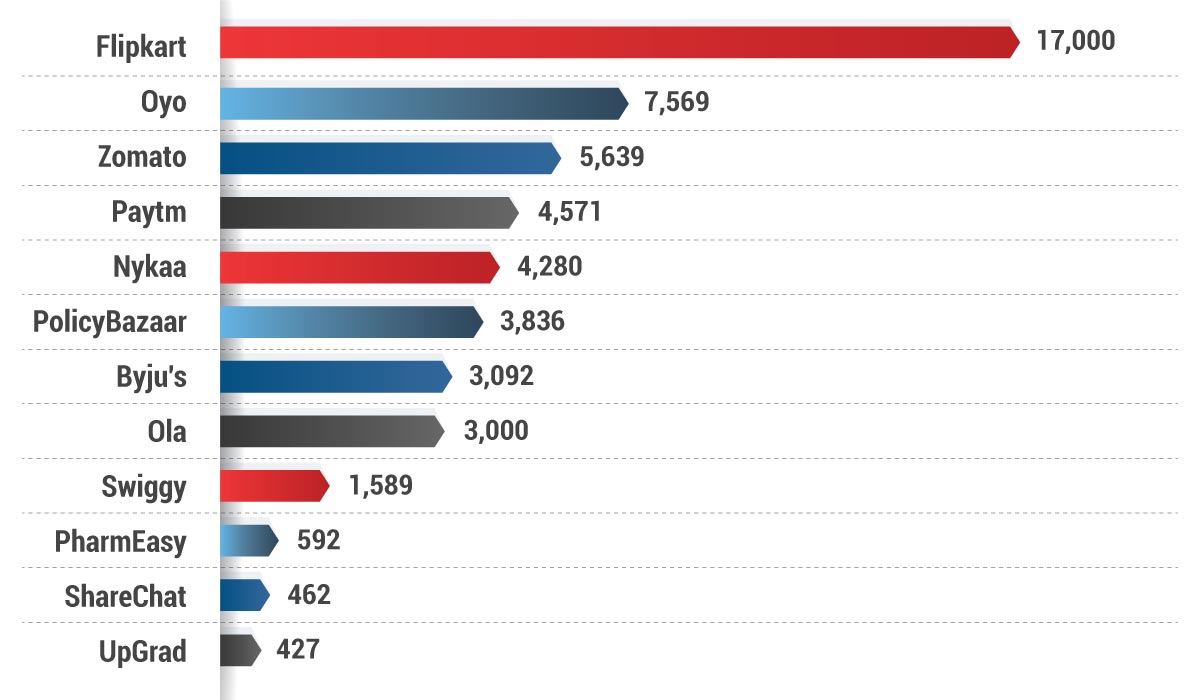 Source: Longhouse Consulting
Source: Longhouse Consulting
Benefits of Introducing ESOP for Startups
- Introducing ESOP in the initial stages of a business is effective when salaries paid by startups may not be at par with industry standards. By offering equity incentives in the form of ESOPs, startups can attract top-tier talent who may be willing to work for lower initial compensation.
- When ESOP benefits are tied to performance, it fosters ownership among employees, reduces staff turnover, enhances loyalty, increases job satisfaction, and finally increases the company’s likelihood of survival.
- ESOP resembles a profit-sharing program, which fosters a sense of ownership among employees. When employees recognize themselves as owners and shareholders, they are inclined to contribute efficiently to the company’s growth and expansion.
- Businesses utilizing ESOP based compensation tend to be more appealing to Venture Capitalist (VC) who appreciates focus on securing top talent while managing costs effectively.
- Under the Companies Act, ESOPs cannot be given to the company’s promoters.
However, for startups recognized by DPIIT, this restriction does not apply. ESOPs can be issued to promoters and directors within 10 years of the startup’s incorporation, even if they hold more than 10% of the company’s shares directly or indirectly. You can read more on eligibility criteria for ESOPs here.
Relief Granted to Eligible Startups
- Under Income Tax Act, 1961 for ESOP Taxation, tax should be deducted at source when employees exercise ESOPs.
- When employees exercise their ESOPs, it can create a cash flow crunch for the company as the startup needs to pay taxes on the value of the options exercised, however, do not receive any new cash from this transaction.
- For eligible startups, the tax payment on the benefit received by the employees when they exercise their stock options (ESOPs) is postponed until one of the following events occurs:
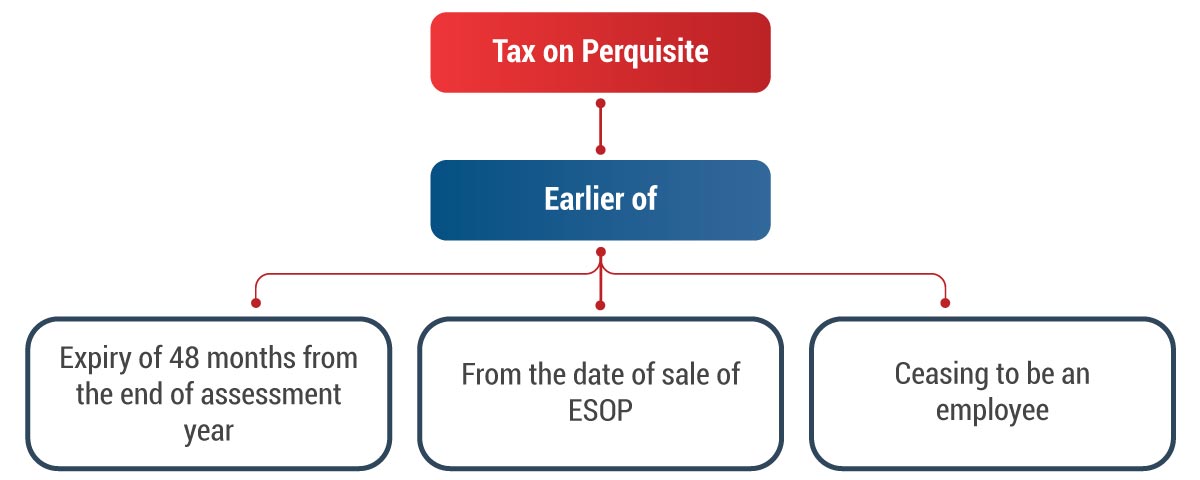
- The start-up should deduct tax within 14 days of triggering any of the above events.
ESOPs as an aid to Protect Founder’s Interest

Related Read: A Complete Guide to Foreign ESOPs for Indian Employees
- As a startup scales through multiple investment rounds, founders may experience dilution of their controlling stake sometimes ranging between 5% and 10%. This reduction in ownership often results in a potential decline in the founders’ enthusiasm to actively contribute to company’s growth. Therefore, to maintain long-term dedication of founders, the management frequently opts to grant additional stakes to the founders through ESOPs aiming to realign their commitment and motivate them to drive the company’s expansion.
- Companies preparing for IPOs generally issue ESOPs to promoters and founders to ensure their interest remains vested in the company. By issuing further ESOPs, companies try to secure the risk of exit of promoter/founder soon after the public listing. This approach safeguards the wealth of knowledge and leadership which are crucial for the success of the company post-public offering.
Importance of ESOP Pool during Venture Capital Funding
- As a startup grows and receives more rounds of investments, the value of existing shareholders may dilute. Below, we have detailed a scenario where the founder and employee A of the startup initially had 90 shares representing 100% holding of the company’s value. Subsequently, after the next round of fundraising the company issues an additional 10 shares to Investor B.
This table showcases the shareholding pattern, pre and post round of fundraising
| Shareholders | Current Shareholding | Post Fundraise | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Shares | Shares in % | No. of Shares |
Shares in %
|
|
| Founder | 70 | 77.78 | 70 | 70 |
| Employee A | 20 | 22.22 | 20 | 20 |
| Investor B | – | – | 10 | 10 |
| Total | 90 | 100 | ||
In view of above, as the total number of shares increased to 100, the shareholding of founder and employee A, who holds 90 shares diluted to 90%, as opposed to the initial 100%, in view of issue of additional shares to Investor B.
- Venture Capital Firms (VCFs) look for startups with ESOP pools prior to securing investment. ESOP pool also consists of shares earmarked for future employee grants. By establishing an ESOP pool in advance, startups gain the ability to promptly allocate shares to current and prospective employees, making the company attractive to top talent and securing further dilution for VCFs.
ESOP Implementation Best Practices
Research indicates that companies that implement ESOPs tend to experience accelerated growth in annual employee expansion and sales growth. Introducing an ESOP in the early stages of company boosts employee engagement, motivation, and contributes to long-term profitability. The right approach of implementing ESOP ensures sustainability and creates an employee-friendly environment for lasting growth.
Things to consider to successfully implement ESOP policy:
- Draft ESOPs with a focus on industry-specific factors such as the type of industry, product/service portfolio, need for technology upgradation, and industry outlook in the coming years.
- Consider the startups’ fundamentals, management’s vision, proposed milestone events, and the ethics of promoters.
- Base ESOPs on a realistic valuation of the startup, considering its current and potential future value.
- When strategizing your hiring needs and determining the size of your ESOP pool, it is crucial to consider the disbursement of ESOPs based on the specific attributes of the employees you intend to recruit. Factors such as skillset, seniority, and potential length of service will influence the distribution of ESOPs.
- Clear communication, employee education, regular monitoring, and legal compliance are essential.
- Encourage employee participation and foster a culture of ownership.
- While drafting an ESOP scheme, startups should scrutinize for potential problematic clauses that may extend ownership rights, especially those tied to prolonged employment periods and similar conditions.
- Startups should actively manage and monitor all ESOPs granted to their employees. This involves maintaining copies of the grant agreements, analyzing the vesting periods, and setting up reminders for expiry dates.
- Ensure timely compliance with all regulations outlined in The Companies Act and Income Tax Act.
- Moreover, there should be a market for startup shares or a well-defined buyback policy to provide employees with realizable value for their ESOPs.
Conclusion
The recent years have witnessed a resurgence of classic ESOP, which ensures the importance of aligning employees with the success of a startup. In the rapidly evolving startup ecosystem, the young workforce no longer considers just cash compensation as attractive. This shift is evident in the introduction of innovative ESOP variants by startups, such as TSOP (Unacademy’s ESOPs for teachers), PSOP (Urban Company’s partner stock option plan for service partners), and MSOPs (BharatPe offering shares to merchants).
These innovative ESOP models are a strategic approach for startups to demonstrate commitment to their workforce and acknowledge the role of employees in success stories. This shift towards equity compensation not only reflects evolving compensation preferences but also showcases the founder’s commitment to people who have played an important role. ESOP buyback has gained popularity over the years and is now frequently seen in the startup ecosystem. Corporate watchers view the ESOP buyback by Flipkart as a well-thought-out plan for building cohesion within the company and creating shared wealth among its employees.
Why Choose InCorp Advisory?
Our team of professionals has expertise in cross-border ESOP tax treatment. Our team specializes in handling the complexities of Indian corporates, foreign exchange, and taxation laws of different countries, ensuring optimized tax solutions for MNCs, startups, and investors. To learn more about our Taxation services, you can write to us at info@incorpadvisory.in or reach out to us at (+91) 77380 66622.
Frequently Asked Question on ESOPs
Yes, start-up should be recognised by DPIIT and hold certificate of eligible business from IMB.
As per Section 192(1C), the tax liability arises within 14 days from any of the following events, whichever is the earliest:
- after the expiry of 48 months from the end of the relevant assessment year; or
- from the date of the sale of such ESOP shares by the assessee; or
- from the date of the taxpayer ceasing to be an employee of the ESOP allotting employer.
Accordingly, employer will be liable for TDS within 14days from the day employee ceases to be an employee.
Yes, total turnover of the business should not exceed one hundred crore rupees for the entire period for which deduction is claimed.
ESOPs vested upto the time of separation/resignation can be exercised within a prescribed time window set by the company and shares can be allotted based on ESOP policy. The options lapse if the employee does not exercise them in that period.
Listing is not the only method of providing an exit to employees. ESOP buyback is also very popular. In this case, employees are rewarded cash, equivalent to the market value of the vested ESOPs instead of allotment of shares.
Share
Share